Serotonin
|
Serotonin is a hormone and neurotransmitter (chemical messenger) found in plants and animals. The chemical name of serotonin is 5-hydroxytryptamine (often abbreviated 5-HT).
In the 1930s, Italian pharmacologist Vittorio Erspamer found a substance capable of causing smooth muscles (e.g., in arteries, intestines, bladder, respiratory tract) to contract. He called this substance enteramine.
In the late 1940s, American scientists Irvine Page, organic chemist Maurice Rapport, and biochemist Arda Green isolated a substance they called serotonin. They named the substance serotonin because it was purified from beef serum (sero-) and was able to increase the tone of blood vessels (-tonin).
In 1952, it was determined that enteramine and serotonin were the same substance. In 1952, American biochemist Betty Mack Twarog found serotonin in the brain of mammals, which brought serotonin into the field of neuroscience (Whitaker-Azmitia, 1999).
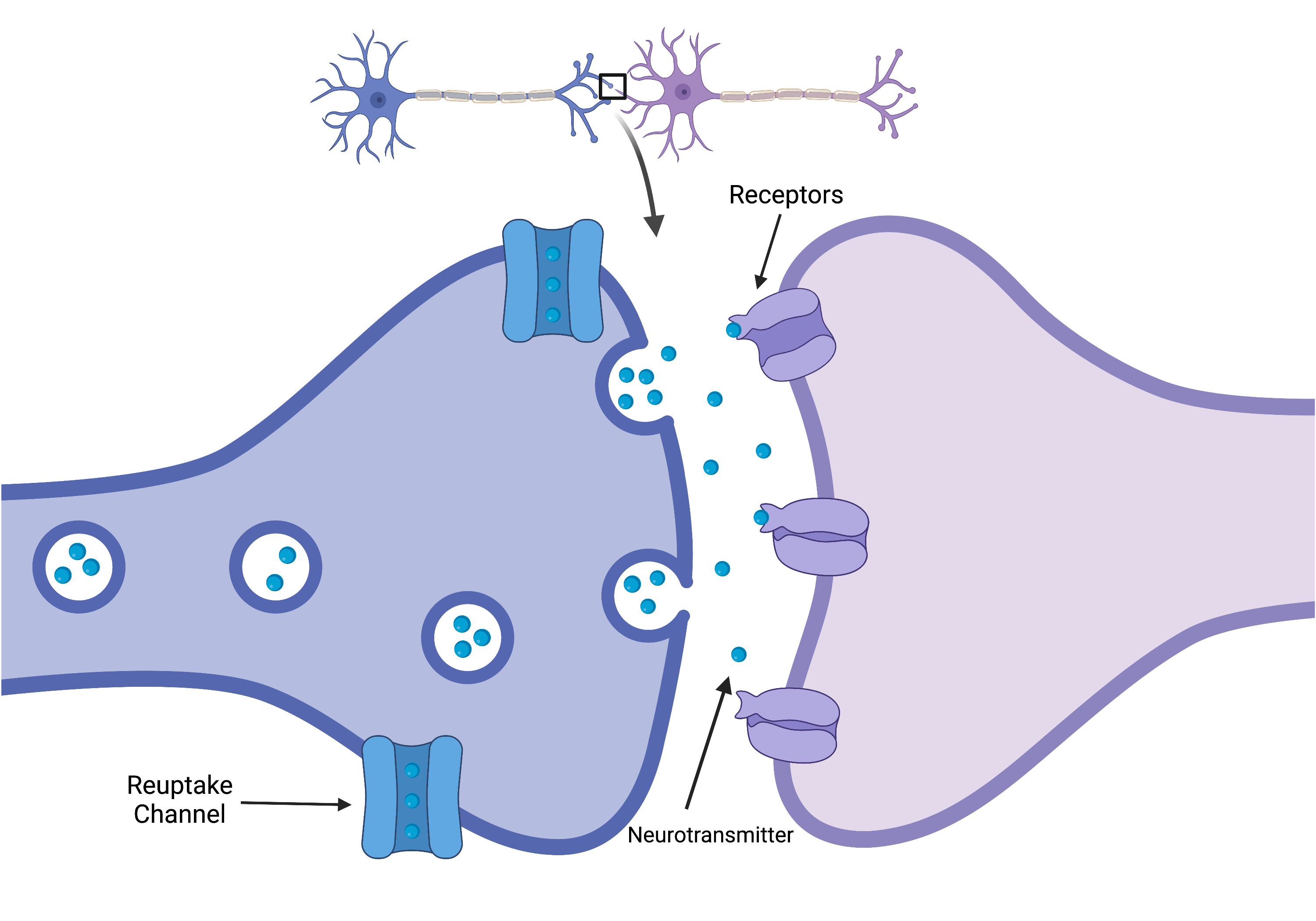
In humans, serotonin affects the central nervous system and has other functions, including cardiovascular, pulmonary, and energy balance. Behavioral and neurological functions modulated by serotonin include mood, sleep, pain perception, reward, fear, anger, aggression, memory, appetite, sexuality, stress response, addiction, and attention (Berger, Gray, & Roth, 2009). Serotonin plays a role in depression, bipolar disorder and anxiety.
In the body, serotonin is derived from the amino acid tryptophan, a substance that occurs naturally in foods such as milk and turkey. The body converts tryptophan into serotonin. Advocates of nutritional treatments for depression suggest increasing dietary tryptophan (either through eating tryptophan-rich foods or consuming dietary supplements) as a treatment for depression.
AntidepressantsOpens in new window that act on serotonin levels or utilization include monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), selective serotonin in reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and others. Atypical antipsychotics and buspirone (used to treat anxiety and depression) also act on the serotonin system (Berger et al., 2009). Hallucinogens (e.g., LSD) affect serotonin levels as do empathogens such as MDMA (Ecstasy).
The herb St. John’s wortOpens in new window, which is sometimes used as a natural treatment for depression, may affect serotonin levels. Combining medications (e.g., SSRIs and St. John’s wort) that affect serotonin levels may result in serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome may include fever, sweating, confusion, restlessness, and tremor (Berger et al., 2009).
- Berger, M., Gray, J.A., & Roth, B. L. (2009). The expanded biology of serotonin. Annual Review of Medicine
- Whitaker-Azmitia, P.M. (1999). The discovery of serotonin and its role in neuroscience. Neuropsycho-pharmacology, 21 (1 Suppl.), 2S – 8S.

