Sexual Characteristics
Secondary Sexual Characteristics in Humans
There are two types of sexual characteristics (or sex characteristics) in human beings: Primary sexual characteristics and Secondary characteristics.
The sexual characteristics which are present at birth are called primary sexual characteristics.
Primary sexual characteristics include internal and external sex organs which are present in babies at the time of their birth.
- The primary sexual characteristics in males (or boys) are: Testes, Penis and Seminal vesicles, etc.
- The primary sexual characteristics in females (or girls) are: Ovaries, Oviducts, Uterus and Vagina, etc.
The primary sexual characteristics are directly involved in reproduction.
The sexual characteristics controlled by hormones which distinguish between sexual mature males and females (sexually mature boys and girls) but are not directly involved in reproduction, are called secondary sexual characteristics.
In secondary sexual characteristics, the body parts (other than sex organs) develop special features which make it easier to distinguish a boy from a girl. For example, the growth of facial hair (like moustache and beard) in boys is a secondary sexual characteristic which helps to distinguish between a mature boy and a girl (because facial hair do not grow in girls).
Similarly, the development of breasts in girls is a secondary sexual characteristic which helps to distinguish a girl from a boy (because boys do not develop breasts).
The secondary sexual characteristics start developing at the time of puberty and continue to develop through the period of adolescence. The main secondary sexual characteristics in males (or boys) are the following:
- Hair grow on face (in the form of moustache and beard) in boys.
- Shoulders and chest broaden (become wider) in boys.
- A deeper voice (or low pitched voice) in boys.
- Adam’s Apple develops in front of throat (or neck) in boys.
The secondary sexual characteristics in boys are produced by the male sex hormone called testosterone, which is made in testes.
The main secondary sexual characteristics in females (or girls) are the following:
- Development of breasts in girls.
- Hips broaden and become more curved and prominent in girls.
- A shrill voice (or high pitched voice) in girls.
The secondary sexual characteristics in girls are produced by the female sex hormone called ‘estrogen’ made in ovaries. We earlier discussed the role of hormones in initiating reproductive functions.
Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
Adolescents become capable of reproduction at puberty when their testes and ovaries begin to produce gametes (sperms and eggs). Adolescent boys grow and become men. Adolescent girls grow and become women.
In men, the capacity to produce male gametes (or sperms) usually lasts throughout life. But in women, the capacity to produce female gametes (eggs or ova) lasts only up to about 45 to 50 years of age.
Due to this, the reproductive phase of life in men (or males) lasts much longer than in women (or females).
We will now discuss the reproductive phase of life in human females (or women) in detail. In females (or women), the reproductive phase of life begins at puberty (10 to 12 years of age) and generally lasts till the age of approximately 45 to 50 years.
With the onset of puberty, the eggs (or ova) begin to mature in the ovaries of a woman. One mature egg (or ovum) is released by one of the ovaries of the woman once in about 28 to 30 days. During this period, the inner lining of uterus grows and becomes thick and spongy, and prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg (Figure X-1). So, in case the fertilized egg cell occurs by a sperm, the fertilized egg cell begins to divide to form an embryo. The embryo then gets embedded in the thick uterus lining. This results in pregnancy which ultimately leads to the birth of a baby. We will now describe what happens if the fertilization of egg cell does not take place.
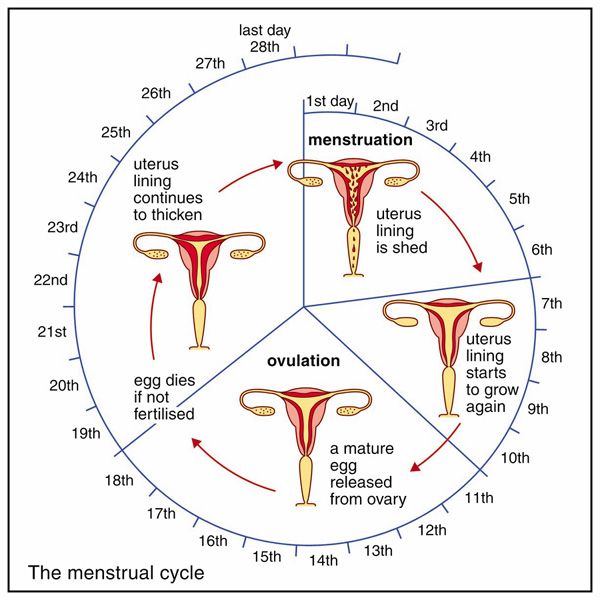 Figure X-1. A thick lining grows in the uterus to receive the fertilized egg cell (if any). In case the egg cell is not fertilized, the thick uterus lining breaks down leading to bleeding. This is called menstruation (or period).
Figure X-1. A thick lining grows in the uterus to receive the fertilized egg cell (if any). In case the egg cell is not fertilized, the thick uterus lining breaks down leading to bleeding. This is called menstruation (or period).
|
If fertilization does not occur (due to lack of sperm), then the egg released by the ovary dies within a few days and the thick lining breaks down (because it is no longer required).
Since the thick uterus lining contains a lot of blood vessels, therefore, the breaking down (or disintegration) of uterus lining produces blood along with other tissues. This blood and other tissues come out of vagina of woman in the form of a “bleeding”.
The bleeding from the uterus which occurs in a woman (or mature girl) every month (if the egg cell has not been fertilized) is called menstrual flow or menstruation.
Menstruation occurs once in about 28 to 30 days (which is almost a month). Menstruation occurs every 28 to 30 days because ovulation (release of egg or ovum by the ovary of woman) occurs after 28 to 30 days. In everyday language, menstruation is called “monthly periods” or just “periods”. It is also called menses. Menstruation (or periods) usually lasts for about 3 to 5 days in a month.
The first menstruation (or menstrual flow) begins at puberty (when the girl or woman is around 10 to 12 years of age).
The first occurrence of menstruation (or periods) at puberty is called “menarche”.
Menarche is the beginning of the reproductive life of a girl (or woman). In other words, menarche is the time from which a girl (or woman) becomes capable of having a baby.
Menstruation stops temporarily when a woman becomes pregnant. Menstruation restarts after the birth of the baby. Menstruation stops permanently when a woman reaches the age of about 45 to 50 years.
With the permanent stoppage of menstruation, a woman loses her ability to bear children. The permanent stoppage of menstruation (or for periods) in a woman is called menopause. Menopause occurs in women at the age of about 45 to 50 years. A woman stops ovulating at menopause and can no longer become pregnant. Menopause is the end of the reproductive life of a woman. We can now say that the reproductive life of a woman starts at menarche and ends at menopause.

