Sterilization
What is Sterilization?

|
Sterilization is a permanent method of birth control obtained via a surgical procedure.
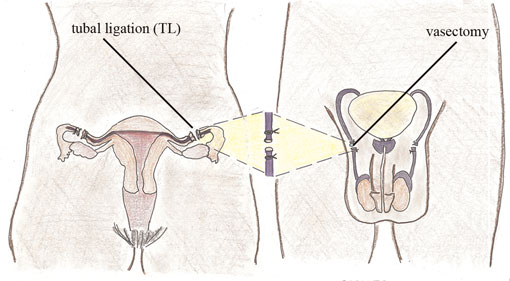
Sterilization procedures for women are called tubal sterilization or female sterilization. The procedure for men is called vasectomy. |
Although in some instances reversal may be accomplished if desired, the procedure to do so is expensive and often not successful. Therefore, those who choose surgical sterilization procedures should consider them permanent.
Female Sterilization
Female sterilization, by tubal ligation or tubal occlusion, involves blocking or ligating (tying) the fallopian tubes.
The procedure may be done immediately after giving birth (within 24 to 48 hours), at the time of an abortion, or during any phase of the menstrual cycle. It can be done using electrocautery or by application of bands or clips via a laparoscopic or minilaparotomy technique.
In 2002, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved injection of an occlusive material into the tubes using a transcervical approach (nonsurgical sterilization, Essure).
During a minilaparotomy, the surgeon makes a small vertical incision in the abdominal wall near the umbilicus. The surgeon brings each tube through the incision and cauterizes the tube, which destroys the tissue.
An alternative is to ligate and then cut each tube. Regional or general anesthesia is required. Oral analgesics are usually sufficient to relieve postoperative discomfort. Although female sterilization is a minor surgical procedure, the postoperative recovery period is about one to two days. The woman should report bleeding or signs of infection.
Nonsurgical sterilization (Essure Permanent Birth Control SystemOpens in new window) is accomplished by using hysteroscopy to guide a tiny metallic implant through the vagina, uterus, and into each fallopian tube. Flexible coils hold the implant in place, and mesh material embedded in the coils of the device causes irritation in the tubes, which respond by causing scar tissue to grow and eventually completely occlude the tubes.
Alternative methods of birth control are required for three months after the procedure to allow time for scar tissue to form and the method to be completely effective at preventing pregnancy.
Advantages of the Essure system include a less invasive procedure than a surgical approach, avoidance of general anesthesia, and the convenience of the physician’s office or clinic. The most common side effects are cramping, nausea, and vomiting. Serious but infrequently occurring side effects include expulsion of the implant and uterine perforation.
Male Sterilization
Male sterilization, vasectomy, can be performed using local anesthesia in an outpatient setting. The procedure takes about 20 minutes to perform. The surgeon makes a small incision on each side of the scrotum over the spermatic cord. The next step is ligation and cutting of each vas deferens.
The surgeon may cauterize the cut ends of the vas deferens and then bury them in the scrotal fascia to reduce the chance of spontaneous reanastomosis. Closure of the skin incisions, often with a single suture, completes the procedure, and a dressing is applied.
The man should expect some pain, bruising, and swelling after the surgery. Rest, the application of an ice pack, scrotal support, and a mild oral analgesic are effective comfort measures.
The surgeon usually recommends moderate inactivity for one to two days because of scrotal tenderness. Removal of the skin sutures occurs about four to seven days after surgery. The man should report any signs of bleeding or infection.
The man may resume sexual intercourse as desired; however, with vasectomy, sterilization is not immediate because sperm remain in the system distal to the ligation. It takes approximately one month to completely purge sperm from the man’s system.
Therefore, it is necessary for the couple to use another method of birth control until a negative sperm count verifies sterility. Vasectomy has no effet on the man’s ability to achieve or maintain erection or on the volume of ejaculation. In addition, there is no interference with the production of testosterone, so secondary sexual characteristics are not affected.
See also:
- Family Planning (Planning & Preventing Pregnancy)Opens in new window
- Natural Contraceptive Methods for Preventing PregnancyOpens in new window
- Fertility Awareness Methods (FAMs)Opens in new window
- Barrier Methods of ContraceptionOpens in new window
- Hormonal Methods of ContraceptionOpens in new window
- Intrauterine Device (IUD)Opens in new window
- Emergency ContraceptionOpens in new window

